
Obesity Surgery
About Obesity
Obesity is defined as a disease that negatively affects the quality and duration of life due to excessive fat mass in the body. Although it does not measure fat directly, the most commonly used method for the measurement of body weight in obesity is division of the person's height (square meter) by the body mass index. According to WHO, over 25 BMI is overweight and over 30 BMI is considered obese.
BMI = < 18.6 Underweight
BMI = 18.6 – 24.9 Normal weight
BMI = 25- 29.9 Overweight
BMI = 30 – 34.9 : 1st degree obesity (class 1 obese)
BMI = 35 – 39.9 : 2nd degree obesity
BMI = > 40 : 3rd degree obesity
Causes of Obesity
Many factors play a role in obesity. Genetic, environmental, psychological, lifestyle, socio-cultural and biochemical factors are related to each other and cause obesity.
Obesity-Caused Diseases:
Obesity Treatment Methods
The aim of obesity treatment is to decrease the risks of morbidity (mortality) and mortality (death) related to obesity by aiming for a realistic body weight loss, to give the individual an adequate and balanced diet habit and to improve the expected life time and quality.
The treatment of obesity is a difficult, long-lasting and continuous process that requires the determination and active participation of the obese person.
Medical Nutrition (Diet) Treatment
Medical nutrition therapy plays a major role in the treatment of obesity.
Slimming diets to be applied should be consistent with adequate and balanced nutrition principles. The aim is to gain the proper eating habit to the patient and to maintain it.
Exercise Therapy
It is recognized that exercise therapy is supportive to medical nutrition therapy and prevents loss of muscle mass when dieting. Exercise therapy helps to reduce weight and prevent weight gain.
Behavior Change Treatment
Behavior change treatment under the control of body weight is a form of treatment that aims to change or decrease the negative behaviors such as over-eating, which causes weight gain, to become a way of life by reinforcing positive behaviors.
Drug Treatment
Drug therapy is one of the methods used to treat obesity and obesity related diseases. These drugs are part of a treatment program that includes medical nutrition therapy, exercise and behavioral therapy. The safety of the drugs used should be determined in terms of health, they should not have significant side effects and addictions in the short and long term, and also, such drugs should be used in the advice and control of physicians.
Surgical treatment
The World Health Organization reports that the most effective treatment for obesity and concomitant diseases is surgery in patients with BMI> 35 kg/m2 and in patients with BMI> 40 kg/m2 without additional disease.
It suggested that obesity and metabolic surgery could be performed in patients with type 2 diabetes with BMI> 30, when drug therapy by the American diabetes association was not sufficient in 2017.
Obesity Surgery Methods;
1. Gastric Balloon
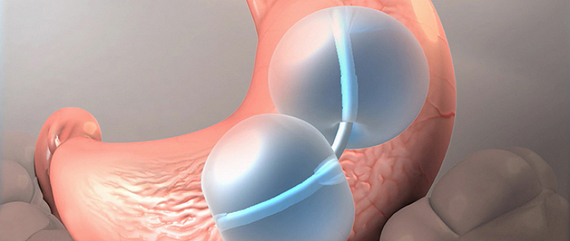
Endoscopically placed inside the stomach, the balloon takes up space in the stomach by being inflated with liquid or air. This reduces the amount of food patient consumes.
Gastric balloon can be applied within 15 to 30 minutes with sedation without requiring general anesthesia. The patient may be discharged after several hours of surveillance. Some patients may need to stay in the hospital for one to three days.
In the early period, the patient may have complaints such as retching, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. These complaints are temporary problems that can be removed with the help of drugs.
The gastric balloon is removed endoscopically after a mean period of 6 months. After the gastric balloon is released, the patient may return to normal life.
For whom is it suitable?
Although it is an appropriate treatment option in patients who do not consider surgical treatment, it is a temporary method. In addition, in 3rd degree obese patients, reduces duration and complications of concomitant heart and lung diseases surgery, providing the pre-operative weight loss.
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy
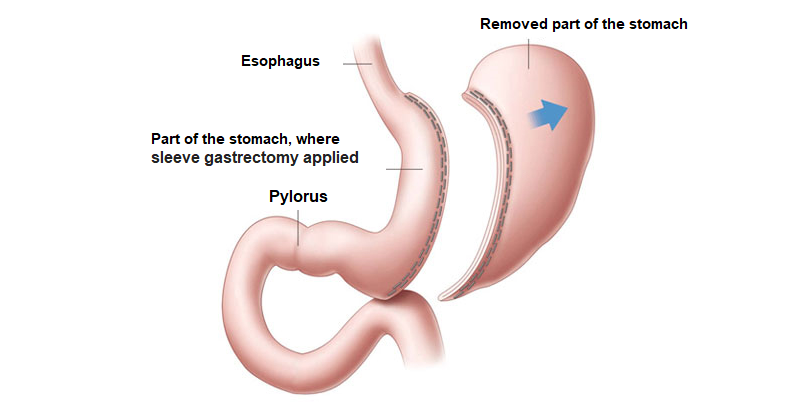
Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery is the process of cutting and removal the left outer part of the stomach. By this method, a stomach of 120-150 ml is formed, food intake to the stomach is restricted and the time to reach the intestine decreases.
Sleeve Gastrectomy is a laparoscopic surgery. The main purpose of Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery is to provide a reduction in food intake by decreasing the volume of the stomach and thus, to reduce the patient's sense of hunger and the patient's weight by decreasing the level of ghrelin hormone secreted from the upper left part of the stomach, which causes a feeling of hunger.
What is Obesity?
Obesity is a disease that negatively affects the quality of life and life expectancy of the body due to the high mass of fat.
How is Obesity Measured?
The most commonly used method is the body mass index obtained by dividing the person's weight by the height. Those whose BMI is over 25 are called overweighted, and those whose BMI is over 30 are called obese.
41% of women and 20.5% of men in Turkey are obese.
Causes of Obesity
Many factors play a role in obesity. Genetic factors, environmental factors, patient’s lifestyle, socio-cultural level, as well as psychological and biochemical factors are related to each other in obesity.
What diseases does obesity cause?
Obesity causes many diseases such as fatty liver, gallbladder diseases, reflux, depression, bone and joint diseases, hypertension, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes.
What is the purpose of obesity treatment?
The aim of obesity treatment is to prevent the occurrence of obesity related diseases by targeting a realistic weight loss and to increase the life quality and duration.
Who are candidates for obesity surgery?
Obese patients with a body mass index greater than 40 or those with a body mass index of 35, who have additional disease such as insulin resistance, hypertension hyperlipidemia, can get benefit from this surgery.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who have a body mass index of more than 30, that is, diabetic patients, can benefit from metabolic surgery if the diabetes cannot be controlled with the help of drug and insulin.
What are the methods and advantages of obesity surgery?
Surgical methods are divided into restrictive and malabsorptive methods. The most commonly used restrictive operations are sleeve gastrectomy surgery and most commonly used malabsorptive surgery is gastric bypass operations.
Obesity operations are comfortable and safe operations which are performed laparoscopically, ie closed manner.
Therefore, the duration of recovery and hospital stay is shorter, postoperative pain is less, cosmetic results are better.
How is the evaluation performed before obesity surgery?
After the preoperative blood tests, lung film, heart electrodes, abdominal usg, upper endoscopy, cardiology, anesthesia and detailed checkup including doctor's opinions, the surgery is decided together with the patient.
Sleeve Gastrectomy surgeries last about 45 minutes - 1 hour.
Since the obesity surgeries are performed by laparoscopic method, patients can drink water and walk the next day.
The patient is discharged 3 or 4 days after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery.
Exercises to be done after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery
Patients can walk 15-20 minutes a week later and can walk 30 minutes briskly after 1 month. After 3 months, they can do sports such as fitness, swimming and running, pilates to increase muscle mass.
What is nutrition after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery?
Especially after sleeve gastrectomy surgeries, patients are fed with liquid food for 3 weeks and can eat soft vegetables between 3rd and 6th weeks. After 6 weeks, they can consume solid foods.
After sleeve gastrectomy surgery, controls should be performed in 1st month, 3rd. month, 6th month and, then, annually.
3. Mini Gastric Bypass

Slevee gastrectomy is performed by forming a thin and long pouch with a volume of 50-100 ml with a thin tube in the stomach. Bowel loop, measured 150-200 cm forward from the beginning of the small intestine (treitz), is connected to the created pouch and anastomosis is performed. In addition to the reduction in the volume of the stomach, the patient loses weight because the food does not pass through the first 150-200 cm of the small intestine. Metabolically associated diseases are taken under control.
4.Roux-Y Gastric By-Pass
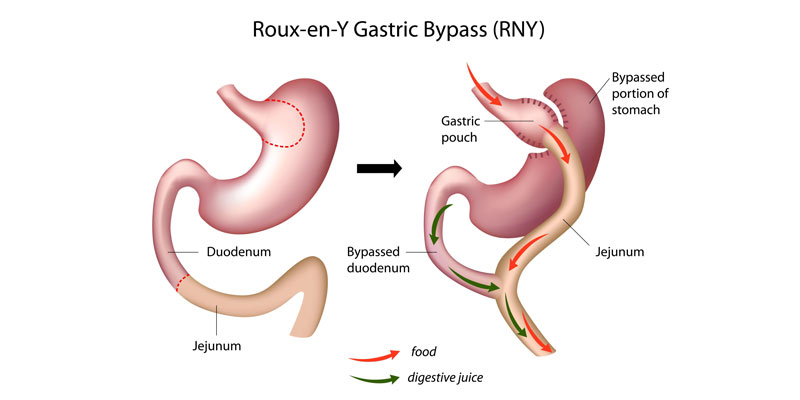
30 ml sac-shaped pouch is formed in the stomach. Anastamosis is carried out by connecting the small intestine to the created pouch. Because of reduced gastric volume and short passage of food in the small intestine, patients get rid of their excess weight. Also, significant success is reached in metabolically type 2 diabetes diseases. Control of diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol levels of patients is provided.
Obesity is defined as a disease that negatively affects the quality and duration of life due to excessive fat mass in the body. Although it does not measure fat directly, the most commonly used method for the measurement of body weight in obesity is division of the person's height (square meter) by the body mass index. According to WHO, over 25 BMI is overweight and over 30 BMI is considered obese.
BMI = < 18.6 Underweight
BMI = 18.6 – 24.9 Normal weight
BMI = 25- 29.9 Overweight
BMI = 30 – 34.9 : 1st degree obesity (class 1 obese)
BMI = 35 – 39.9 : 2nd degree obesity
BMI = > 40 : 3rd degree obesity
Causes of Obesity
Many factors play a role in obesity. Genetic, environmental, psychological, lifestyle, socio-cultural and biochemical factors are related to each other and cause obesity.
Obesity-Caused Diseases:
- Hypertension
- Insulin resistance
- Type 2 diabetes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Coronary artery disease
- Depression
- Reflux
- Diseases of gallbladder
- Pulmonary diseases
- Endometrial, ovarian and breast cancers in women
- Colon and prostate cancers in men
- Osteoarthritis, sleep apnea, fatty liver
Obesity Treatment Methods
The aim of obesity treatment is to decrease the risks of morbidity (mortality) and mortality (death) related to obesity by aiming for a realistic body weight loss, to give the individual an adequate and balanced diet habit and to improve the expected life time and quality.
The treatment of obesity is a difficult, long-lasting and continuous process that requires the determination and active participation of the obese person.
Medical Nutrition (Diet) Treatment
Medical nutrition therapy plays a major role in the treatment of obesity.
Slimming diets to be applied should be consistent with adequate and balanced nutrition principles. The aim is to gain the proper eating habit to the patient and to maintain it.
Exercise Therapy
It is recognized that exercise therapy is supportive to medical nutrition therapy and prevents loss of muscle mass when dieting. Exercise therapy helps to reduce weight and prevent weight gain.
Behavior Change Treatment
Behavior change treatment under the control of body weight is a form of treatment that aims to change or decrease the negative behaviors such as over-eating, which causes weight gain, to become a way of life by reinforcing positive behaviors.
Drug Treatment
Drug therapy is one of the methods used to treat obesity and obesity related diseases. These drugs are part of a treatment program that includes medical nutrition therapy, exercise and behavioral therapy. The safety of the drugs used should be determined in terms of health, they should not have significant side effects and addictions in the short and long term, and also, such drugs should be used in the advice and control of physicians.
Surgical treatment
The World Health Organization reports that the most effective treatment for obesity and concomitant diseases is surgery in patients with BMI> 35 kg/m2 and in patients with BMI> 40 kg/m2 without additional disease.
It suggested that obesity and metabolic surgery could be performed in patients with type 2 diabetes with BMI> 30, when drug therapy by the American diabetes association was not sufficient in 2017.
Obesity Surgery Methods;
- Gastric Balloon
- Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Mini Gastric Bypass
- Roux- y Gastric Bypass
1. Gastric Balloon

Endoscopically placed inside the stomach, the balloon takes up space in the stomach by being inflated with liquid or air. This reduces the amount of food patient consumes.
Gastric balloon can be applied within 15 to 30 minutes with sedation without requiring general anesthesia. The patient may be discharged after several hours of surveillance. Some patients may need to stay in the hospital for one to three days.
In the early period, the patient may have complaints such as retching, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. These complaints are temporary problems that can be removed with the help of drugs.
The gastric balloon is removed endoscopically after a mean period of 6 months. After the gastric balloon is released, the patient may return to normal life.
For whom is it suitable?
Although it is an appropriate treatment option in patients who do not consider surgical treatment, it is a temporary method. In addition, in 3rd degree obese patients, reduces duration and complications of concomitant heart and lung diseases surgery, providing the pre-operative weight loss.
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy

Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery is the process of cutting and removal the left outer part of the stomach. By this method, a stomach of 120-150 ml is formed, food intake to the stomach is restricted and the time to reach the intestine decreases.
Sleeve Gastrectomy is a laparoscopic surgery. The main purpose of Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery is to provide a reduction in food intake by decreasing the volume of the stomach and thus, to reduce the patient's sense of hunger and the patient's weight by decreasing the level of ghrelin hormone secreted from the upper left part of the stomach, which causes a feeling of hunger.
What is Obesity?
Obesity is a disease that negatively affects the quality of life and life expectancy of the body due to the high mass of fat.
How is Obesity Measured?
The most commonly used method is the body mass index obtained by dividing the person's weight by the height. Those whose BMI is over 25 are called overweighted, and those whose BMI is over 30 are called obese.
41% of women and 20.5% of men in Turkey are obese.
Causes of Obesity
Many factors play a role in obesity. Genetic factors, environmental factors, patient’s lifestyle, socio-cultural level, as well as psychological and biochemical factors are related to each other in obesity.
What diseases does obesity cause?
Obesity causes many diseases such as fatty liver, gallbladder diseases, reflux, depression, bone and joint diseases, hypertension, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes.
What is the purpose of obesity treatment?
The aim of obesity treatment is to prevent the occurrence of obesity related diseases by targeting a realistic weight loss and to increase the life quality and duration.
Who are candidates for obesity surgery?
Obese patients with a body mass index greater than 40 or those with a body mass index of 35, who have additional disease such as insulin resistance, hypertension hyperlipidemia, can get benefit from this surgery.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who have a body mass index of more than 30, that is, diabetic patients, can benefit from metabolic surgery if the diabetes cannot be controlled with the help of drug and insulin.
What are the methods and advantages of obesity surgery?
Surgical methods are divided into restrictive and malabsorptive methods. The most commonly used restrictive operations are sleeve gastrectomy surgery and most commonly used malabsorptive surgery is gastric bypass operations.
Obesity operations are comfortable and safe operations which are performed laparoscopically, ie closed manner.
Therefore, the duration of recovery and hospital stay is shorter, postoperative pain is less, cosmetic results are better.
How is the evaluation performed before obesity surgery?
After the preoperative blood tests, lung film, heart electrodes, abdominal usg, upper endoscopy, cardiology, anesthesia and detailed checkup including doctor's opinions, the surgery is decided together with the patient.
Sleeve Gastrectomy surgeries last about 45 minutes - 1 hour.
Since the obesity surgeries are performed by laparoscopic method, patients can drink water and walk the next day.
The patient is discharged 3 or 4 days after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery.
Exercises to be done after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery
Patients can walk 15-20 minutes a week later and can walk 30 minutes briskly after 1 month. After 3 months, they can do sports such as fitness, swimming and running, pilates to increase muscle mass.
What is nutrition after Sleeve Gastrectomy surgery?
Especially after sleeve gastrectomy surgeries, patients are fed with liquid food for 3 weeks and can eat soft vegetables between 3rd and 6th weeks. After 6 weeks, they can consume solid foods.
After sleeve gastrectomy surgery, controls should be performed in 1st month, 3rd. month, 6th month and, then, annually.
3. Mini Gastric Bypass

Slevee gastrectomy is performed by forming a thin and long pouch with a volume of 50-100 ml with a thin tube in the stomach. Bowel loop, measured 150-200 cm forward from the beginning of the small intestine (treitz), is connected to the created pouch and anastomosis is performed. In addition to the reduction in the volume of the stomach, the patient loses weight because the food does not pass through the first 150-200 cm of the small intestine. Metabolically associated diseases are taken under control.
4.Roux-Y Gastric By-Pass

30 ml sac-shaped pouch is formed in the stomach. Anastamosis is carried out by connecting the small intestine to the created pouch. Because of reduced gastric volume and short passage of food in the small intestine, patients get rid of their excess weight. Also, significant success is reached in metabolically type 2 diabetes diseases. Control of diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol levels of patients is provided.
Share




